Το καλάθι σας
Το καλάθι σας είναι άδειο
Ειδήσεις Για Την Εταιρεία Μας
Τα Μπαχαρικά μας
Η ζάχαρή μας
Τα Καπάκια μας
-
 Kegcaps 69 mm, Green 147 Grundey G-type (850/box)
Προσθέστε
Kegcaps 69 mm, Green 147 Grundey G-type (850/box)
Προσθέστε
-
 Crown Caps 26 mm TFS-PVC Free, Red col. 2941 (10000/box)
Προσθέστε
Crown Caps 26 mm TFS-PVC Free, Red col. 2941 (10000/box)
Προσθέστε
-
 Kegcaps 64 mm, Red 150 Sankey S-type (EU) (1000/box)
Προσθέστε
Kegcaps 64 mm, Red 150 Sankey S-type (EU) (1000/box)
Προσθέστε
-
 Crown Caps 26mm TFS-PVC Free, Orange col. 2605 (10000/box)
Προσθέστε
Crown Caps 26mm TFS-PVC Free, Orange col. 2605 (10000/box)
Προσθέστε
-
 Kegcaps 64 mm, Beige 65 Sankey S-type (EU) (1000/box)
Προσθέστε
Kegcaps 64 mm, Beige 65 Sankey S-type (EU) (1000/box)
Προσθέστε
Γλωσσάριο
Rays of short wavelengths ranging from 0.06 to 2 Angstrom units, which are emitted by suddenly changing the velocity of a moving electric charge by impact of a cathode ray on a target in a vacuum tube and by the changes in the atoms of the target caused by the impact. Also called Roentgen rays.
A pentose sugar present in small quantities in wort. Relatively unimportant in brewing.






![ΆΡΚΕΥΘΡΩΝ (ΚΑΡΠΟΙ) [JUNIPER BERRIES] (5KG)](https://www.castlemalting.com/Publications/SpiceProducts/Images/Small/GenevrierBaie.jpg)







 Slovenian hops Pesticide Residues Certificate (Crop 2022)
Slovenian hops Pesticide Residues Certificate (Crop 2022)
 Hollands Hophuis, Confirmation Statement Organic Hops 2021
Hollands Hophuis, Confirmation Statement Organic Hops 2021
 Crown Caps Finnkorkki Statement
Crown Caps Finnkorkki Statement
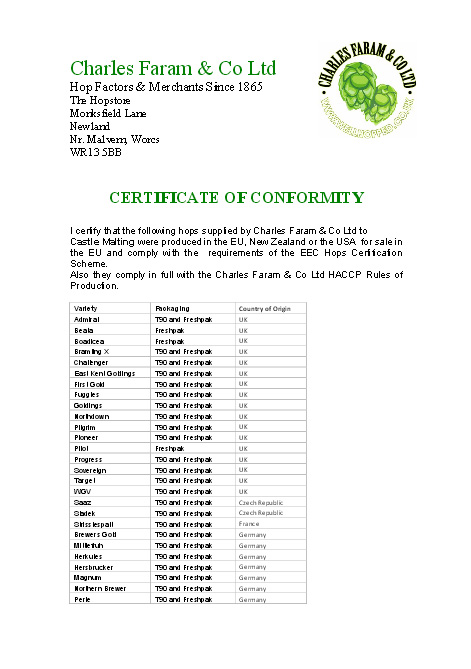 ChF Hops Conformity Certificate
ChF Hops Conformity Certificate
 Fermentis Yeast Food Safety Certificate
Fermentis Yeast Food Safety Certificate



